There are six types of envelope syntaxes recognized by the EnvelopeString class: CLM, LISP, MUSICKIT, MATHEMATICA, PLAIN, and SIG.
(0 0 0.496 0.697 0.661 0.460 0.726 0.878 1 0)
((0.000 0.000)(0.496 0.697)(0.661 0.460)(0.726 0.878)(1.000 0.000))
For the EnvelopeString class, you may optionally add commas between numbers. The default interpolation type for LISP envelopes is linear interpolation.
[(0,0)(0.496,0.697)(0.661,0.460)(0.726,0.878)|(1,0)]
For the EnvelopeString class, it is unimportant whether you include the commas in the envelope when calling the setEnvelope function. The default interpolation type for MusicKit envlopes is linear interpolation. If a stick point is included in the envelope, then time in envelope is described in seconds.
{{0, 0},{0.496, 0.697},{0.661, 0.460},{0.726, 0.878},{1, 0}}
0, 0, 0.496, 0.697, 0.661, 0.460, 0.726, 0.878, 1, 0
G(0 0 L; 0.5, 0.7; 0.7 0.5; 0.8 0.9; s; 1.0 0.0)t
If a stick point is used, then an optional character following the
closing ')' of the envelope will specify if the time units of the
envelope represent time in seconds ('t'), or samples ('m'). The
default is 'm'. Spacing in all envelopes is unimportant.
Types of interpolation recognized by a sig envelope:
C = Constant interpolation: there is no interpolation between the
current envelope point and the following point. Use just the
value of the last point.
L = Linear interpolation.
G = Geometric interpolation.
H = Harmonic interpolation (not yet implemented).
K = Turkey interpolation (not yet implemented).
B = Cubic interpolation (not yet implemented).
X = Exponential (MusicKit) interpolation (not yet implemented).
Other types of envelopes which may be allowed in the future:
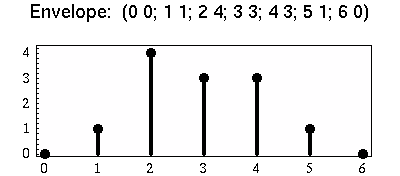
Envelopes describe a function with a discrete set of points. Here for example, is a set of envelope points:

These envelope points can be used with various interpolation types to generate a continuous function which gives dependent values for any unspecified independent values.
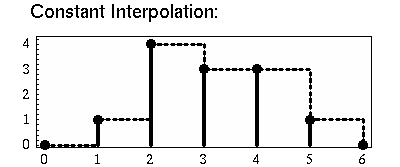
Constant interpolation does not alter the dependent value(s) of the previous point until a new point is reached:
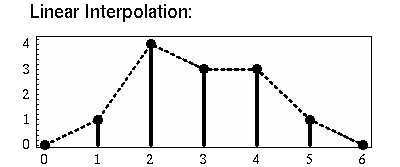
Linear interpolation draws straight lines between the envelope points:
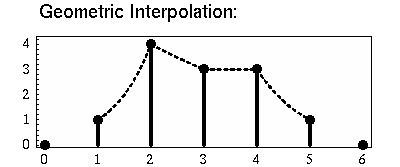
Geometric interpolation draws straight lines between points on a log scale (on the y-axis), but when converting back to a linear scale, the lines curve:
The Envelope format types are integers. Here are the defines for each type of envelope syntax:
Unknown Envelope UNKNOWN_ENV (0)
CLM Envelope CLM_ENV (1)
LISP Envelope LISP_ENV (2)
MusicKit Envelope MUSICKIT_ENV (3)
MK_ENV (3)
Mathematica Envelope MATHEMATICA_ENV (4)
MMA_ENV (4)
Plain Envelope PLAIN_ENV (5)
Sig Envelope SIG_ENV (6)